Cell Structure and Function
Key Ideas:
-
Understand that the cell is the smallest unit of independent life
-
Explain the significance of surface area to volume ratio in cells
-
Compare the size and structure of prokaryote and eukaryote cells
-
Compare the structures of animal and plant eukaryote cells
-
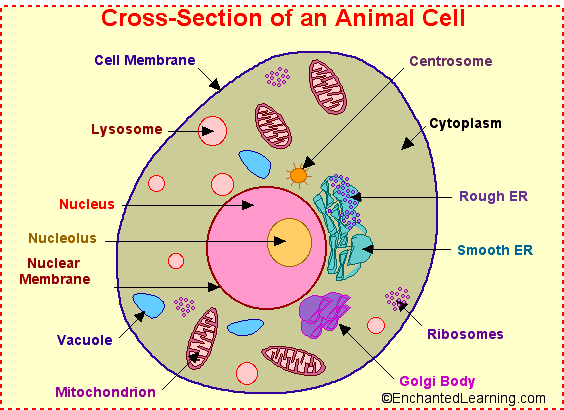
Describe the structure and function of the following organelles: nucleus, mitochondria, vacuole, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum





A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of living organisms, which can exist on its own. It is sometimes called the building block of life.
They are small structures bounded by a membrane and inside contain smaller strucutres that enable cells to perform their function.
Some organisms consist of only a single cells - these are called unicelluar.
If an organism consists of more than 1 cell it is called multicellular. Humans are multicelluar as we have trillions of cell that make up our body.
Understand that the cell is the smallest unit of independent life
What does it mean that it is living?
Things that are alive are able to reproduce, respond to stimuli in their environment and transform energy into forms that allow them to perform these functions.
Explain the significance of surface area to volume ratio in cells
Surface area (SA): is that size of the external area
Volume (V): is the 3D space it occupies
Surface area to volume ratio (SA:V): is the amount of surface a object has relative to its volume
So whats this got to do with cells?
The surface area to volume ratio DECREASES as an object gets bigger. That means that the bigger the object the less surface area there is in relation to its volume. The smaller the object the more surface area there is in relation to its volume.

Surface area to volume ratio can help us to answer the question- Why are cells so small?
Cells must exchnge materials with their external environment eg. glucose and oxygen and obtained from the external environment and carbon dioxide is released into it. All these materials have to pass through the cell membrane.
The larger the surface area of a cell the more materials that can be exchanged in a cell.
Compare eukayrotic and prokaryotic cells
Compare plant and animal cells




